
As a result, the point (x, y) is reflected across the X-axis (x, -y). The Y-coordinates, on the other hand, is changed to the opposite sign. The x-coordinates of a point remains the same when it is reflected across the X-axis. The reflection transformation might be performed to both the X and Y axes. There is 1 line that helps in reflecting the object and this line is said to be the line of reflection. Since the position is changed in this transformation, there are chances for Translation as well.īoth the figures (before and after reflection) are equidistant from all their points over their surfaces. However, the size and shape remain the same. Only the direction of the resulting image is the opposite. So, the resulting image will be the mirror image to the origins structure. Now, let us learn the reflection definition by using the following pointers for a better understanding.įlipping an image is called a Reflection in geometry. We understood what a mathematical transformation. Important Points Regarding the ‘Reflection’ Definition The reflection of point P through line AB is then pointed to Q. The points of intersection of these two circles will be P and Q. Step 2 (green): Make circles with a radius of r that are centred at A′ and B′. Step 1 (red): Create points A′ and B′ on line AB that are equidistant from P by constructing a circle with the centre at P and a fixed radius r. Using a compass and a straightedge, reflect point P through the line AB as follows (see figure): To locate the figure's reflection, reflect on each point in the figure. A reflection through a point, for example, is an involutive isometry with only one fixed point the image of the letter p beneath it would appear to be a point d.ĭrop a 90 degree line from the point to the line (plane) used for reflection and extend it the same distance on the opposite side to determine the reflection of a point in a plane (or, equivalently, 3-dimensional) geometry. The collection of fixed points (the "mirror") in such isometries is an affine subspace that is possibly smaller than a hyperplane. The term "reflection" is frequently used to refer to a broader class of mappings from a Euclidean space to itself, notably involutions, which are non-identity isometries. The letters ABC and A'B'C' stand for pre-image and image, respectively. The original image is referred to as a pre-image, and its reflection is referred to as an image. The translation may occur as a result of changes in position during reflection. The reflected picture should have the same shape and size as the original, but it should face the opposite way. If a figure is stated to be a mirror of another figure, then each point in the first figure is equidistant from the corresponding point in the second figure. The line of reflection is a line along which an image reflects. A mirror image of a shape is called a reflection. Let's look at the definition of reflection transformation in math, reflection formula, reflections on the coordinate plane, and examples.Ī flip is a term used in mathematical geometry to describe a reflection. The four fundamental transformations are as follows:
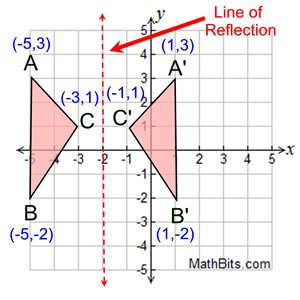
One of the four types of transformations in geometry is reflection. A reflection is an involution in which every point returns to its original place and every geometrical object is returned to its original state when applied twice in succession. Its reflection in a horizontal axis would produce picture b. For example, for a reflection about a vertical axis, the mirror image of the minuscule Latin letter p would be q. A figure's mirror image in the axis or plane of reflection is called a reflection image or reflection point. The relationship between reflection lines and highlight lines is likened to that between specular and diffuse shading.The reflection meaning in mathematics, a reflection (sometimes spelt reflexion) is an isometric mapping from a Euclidean space to itself that uses a hyperplane as a collection of fixed points this set is known as the axis (in dimension 2) or plane (in dimension 3). Reflection lines visualized on surfaces completed using a biharmonic and triharmonic equation with C 1


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
